




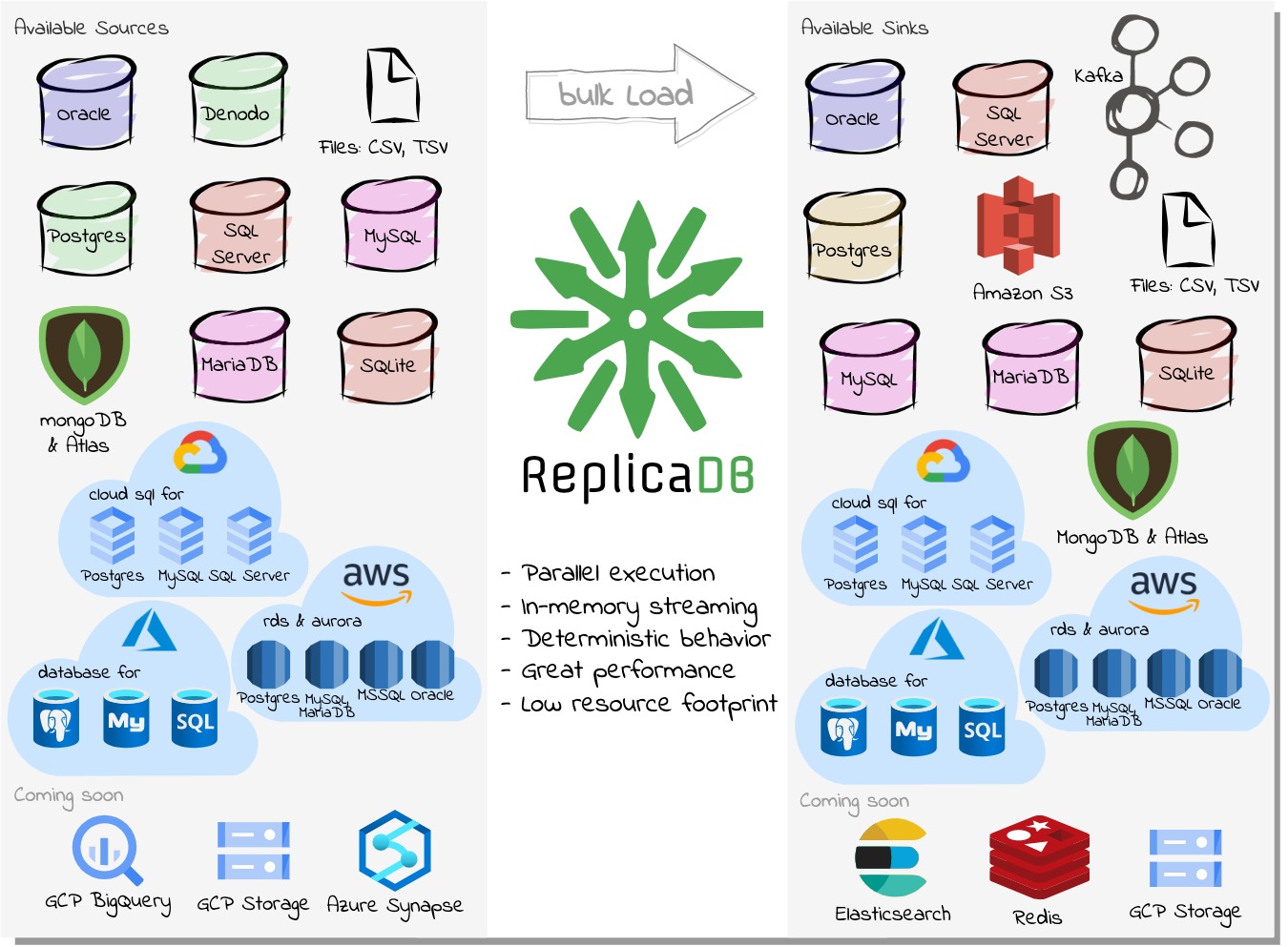
ReplicaDB is a high-performance, open-source command-line tool for bulk data replication between heterogeneous databases. It enables efficient ETL/ELT workflows by transferring data in parallel between Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, SQL Server, and other databases without requiring database agents or triggers.
ReplicaDB supports a wide range of data sources including relational databases (Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, SQL Server, SQLite, IBM DB2 LUW and DB2 for i), NoSQL databases (MongoDB), data virtualization platforms (Denodo), file formats (CSV), cloud storage (Amazon S3), and streaming platforms (Kafka). Any JDBC-compliant database is also supported with some limitations.
The tool is cross-platform compatible with Windows, Linux, and macOS, and leverages parallel data transfer for optimal performance and system utilization during large-scale data migrations and synchronization tasks.
Why ReplicaDB
ReplicaDB addresses common gaps in existing database replication tools by providing:
- Open Source: Transparent development and community-driven improvements
- Cross-Platform: Java-based solution compatible with Linux, Windows, and macOS
- Heterogeneous Support: Works with SQL, NoSQL, and persistent stores like CSV, Amazon S3, or Kafka
- Simple Architecture: Standalone command-line tool without requiring database agents
- High Performance: Optimized for bulk data transfer with large datasets
- Non-Intrusive: Focused on batch replication without requiring database triggers or CDC installation
Comparison with Alternatives
Common alternatives and how ReplicaDB differs:
- SymmetricDS: A comprehensive CDC solution with database triggers. While feature-rich, it requires installation and maintenance of capture tables in source databases, making it more intrusive for batch replication scenarios.
- Sqoop: Designed specifically for Hadoop ecosystems, limiting its use in other environments where Hadoop infrastructure is not available.
- Pentaho and Talend: Full-featured ETL platforms that require custom development for each replication job, increasing complexity and maintenance overhead for straightforward data transfer tasks.
Feature Comparison
| Feature | SymmetricDS | Sqoop | Pentaho/Talend | ReplicaDB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Database Agents Required | Yes | No | No | No |
| Triggers in Source DB | Yes | No | No | No |
| Heterogeneous Databases | Limited | No | Yes | Yes |
| Hadoop Requirement | No | Yes | No | No |
| Custom Development per Job | Low | Low | High | None |
| Parallel Transfer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Open Source | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Installation
Prerequisites
Before installing ReplicaDB, ensure you have:
- Java Runtime: Java JDK or JRE 11 or higher installed and configured
- Network Connectivity: Reliable network access to both source and sink databases
- Database Credentials: Appropriate permissions on both databases:
- Source database: SELECT permissions on tables to replicate
- Sink database: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and CREATE TABLE permissions
- (Optional) Docker or Podman for containerized deployment
Stand Alone
System Requirements
ReplicaDB is written in Java and requires a Java Runtime Environment (JRE) Standard Edition (SE) or Java Development Kit (JDK) Standard Edition (SE) version 11 or above. The minimum system requirements are:
- Java SE Runtime Environment 11 or above
- Memory - 256 MB minimum, 1 GB recommended for large datasets
Install
Download the latest release from GitHub and extract the archive:
$ curl -o ReplicaDB-0.18.0.tar.gz -L "https://github.com/osalvador/ReplicaDB/releases/download/v0.18.0/ReplicaDB-0.18.0.tar.gz"
$ tar -xvzf ReplicaDB-0.18.0.tar.gz
$ ./bin/replicadb --help
JDBC Drivers
ReplicaDB already comes with all the JDBC drivers for the Compatible Databases. But you can use ReplicaDB with any JDBC-compliant database.
First, download the appropriate JDBC driver for the type of database you want to use, and install the .jar file in the $REPLICADB_HOME/lib directory. Each driver .jar file also has a specific driver class that defines the entry-point to the driver.
If your database is JDBC-compliant and not appear in the Compatible Databases list, you must set the driver class name in the configuration properties as extra JDBC parameter.
For example, to replicate a DB2 database table as both source and sink
######################## ReplicadB General Options ########################
mode=complete
jobs=1
############################# Source Options ##############################
source.connect=jdbc:db2://localhost:50000/testdb
source.user=${DB2USR}
source.password=${DB2PASS}
source.table=source_table
source.connect.parameter.driver=com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2Driver
############################# Sink Options ################################
sink.connect=jdbc:db2://localhost:50000/testdb
sink.user=${DB2USR}
sink.password=${DB2PASS}
sink.table=sink_table
sink.connect.parameter.driver=com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2Driver
Docker
For containerized deployments or environments without Java installed, ReplicaDB is available as a Docker image.
$ docker run \
-v /tmp/replicadb.conf:/home/replicadb/conf/replicadb.conf \
osalvador/replicadb
Visit the project homepage on Docker Hub for more information.
Podman
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Fedora environments, ReplicaDB provides a container image based on Red Hat Universal Base Image (UBI) 8, which is optimized for enterprise security and compliance.
$ podman run \
-v /tmp/replicadb.conf:/home/replicadb/conf/replicadb.conf:Z \
osalvador/replicadb:ubi8-latest
Note: The :Z flag relabels the volume for SELinux compatibility. See Podman documentation for details on volume mounting with SELinux.
Full Documentation
You can find the full ReplicaDB documentation here: Docs
Configuration Wizard
You can create a configuration file for a ReplicaDB process by filling out a simple form: ReplicaDB configuration wizard
Quick Start Examples
Oracle to PostgreSQL
Security Note: The examples below use environment variables for credentials. Never hard-code passwords in scripts or command history.
Prerequisites:
- Source table must exist and be accessible with SELECT permissions
- Sink table must exist with a compatible schema
- For
incrementalmode, sink table must have primary keys defined
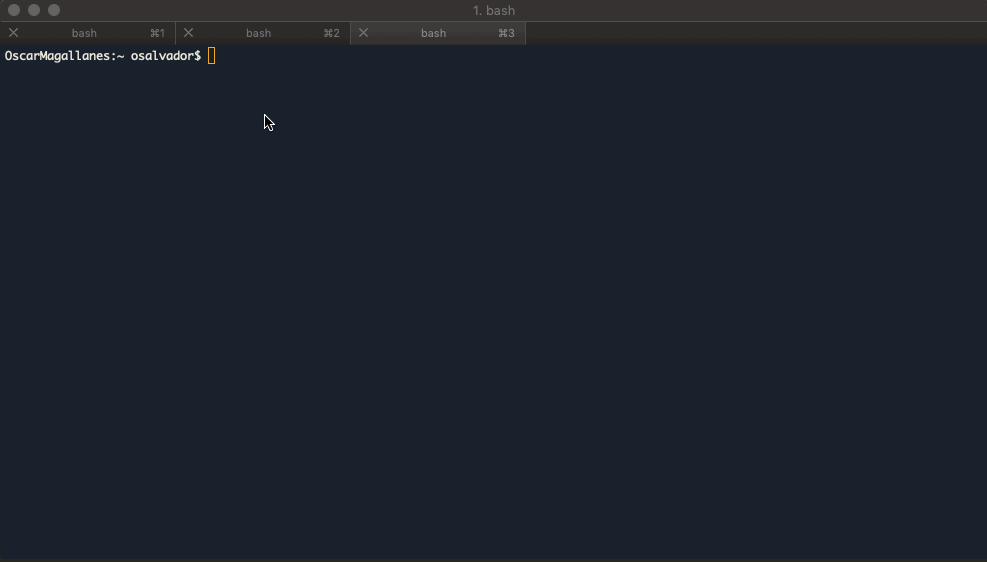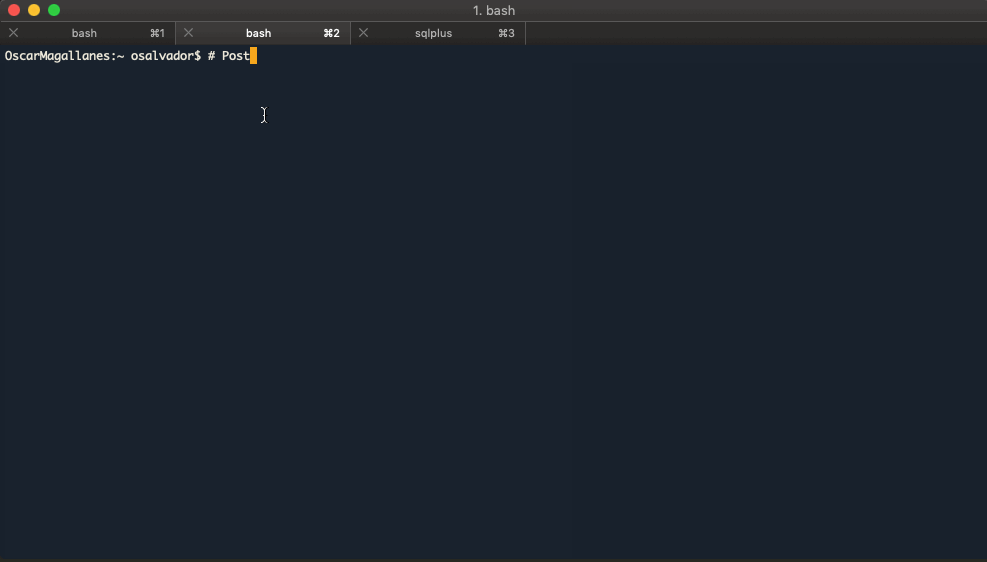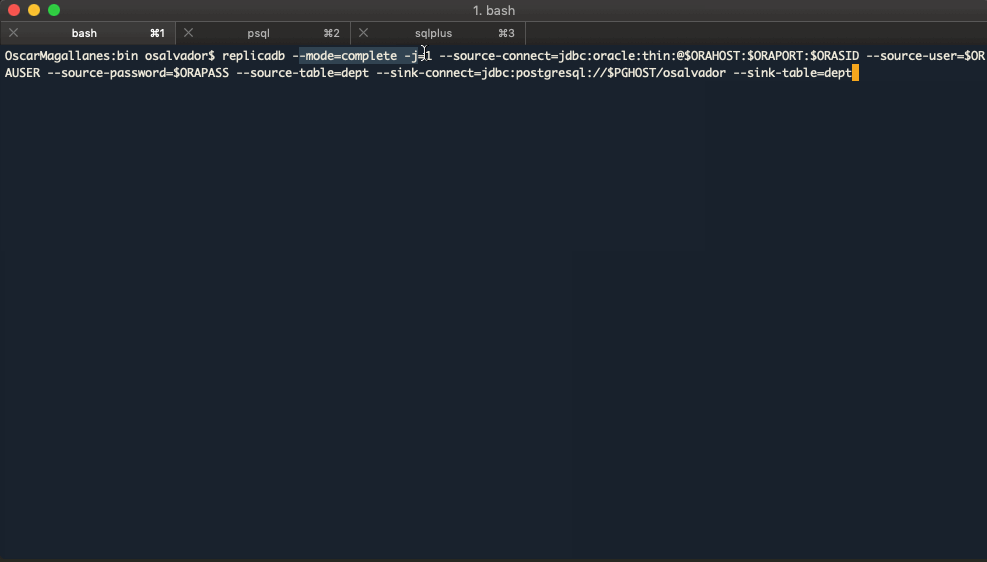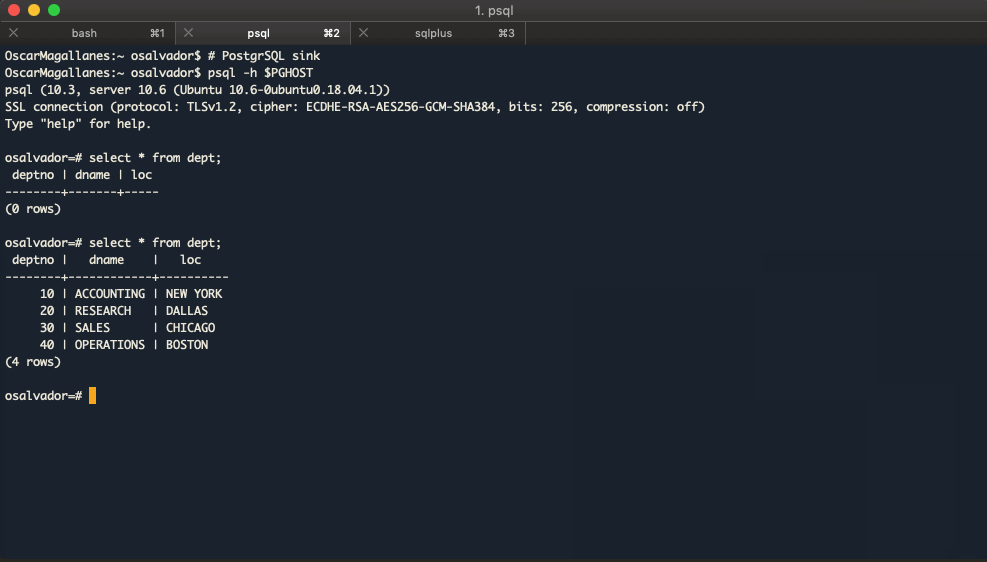
$ replicadb --mode=complete -j=1 \
--source-connect=jdbc:oracle:thin:@//$ORAHOST:$ORAPORT/$SERVICE_NAME \
--source-user=$ORAUSER \
--source-password=$ORAPASS \
--source-table=dept \
--sink-connect=jdbc:postgresql://$PGHOST/osalvador \
--sink-table=dept
2026-01-28 10:15:23,808 INFO ReplicaTask:36: Starting TaskId-0
2026-01-28 10:15:24,650 INFO SqlManager:197: TaskId-0: Executing SQL statement: SELECT /*+ NO_INDEX(dept)*/ * FROM dept where ora_hash(rowid,0) = ?
2026-01-28 10:15:24,650 INFO SqlManager:204: TaskId-0: With args: 0,
2026-01-28 10:15:24,772 INFO ReplicaDB:89: Total process time: 1302ms
Alternatively, use a configuration file to simplify repeated operations:
######################## ReplicadB General Options ########################
mode=complete
jobs=1
############################# Source Options ##############################
source.connect=jdbc:oracle:thin:@//${ORAHOST}:${ORAPORT}/${SERVICE_NAME} # You can also use SID format here ${ORASID}
source.user=${ORAUSER}
source.password=${ORAPASS}
source.table=dept
############################# Sink Options ################################
sink.connect=jdbc:postgresql://${PGHOST}/osalvador
sink.table=dept
$ replicadb --options-file replicadb.conf
PostgreSQL to Oracle
$ replicadb --mode=complete -j=1 \
--sink-connect=jdbc:oracle:thin:@//$ORAHOST:$ORAPORT/$SERVICE_NAME \
--sink-user=$ORAUSER \
--sink-password=$ORAPASS \
--sink-table=dept \
--source-connect=jdbc:postgresql://$PGHOST/osalvador \
--source-table=dept \
--source-columns=dept.*
2026-01-28 10:20:35,334 INFO ReplicaTask:36: Starting TaskId-0
2026-01-28 10:20:35,440 INFO SqlManager:131 TaskId-0: Executing SQL statement: SELECT * FROM dept OFFSET ?
2026-01-28 10:20:35,441 INFO SqlManager:204: TaskId-0: With args: 0,
2026-01-28 10:20:35,550 INFO OracleManager:98 Inserting data with this command: INSERT INTO /*+APPEND_VALUES*/ ....
2026-01-28 10:20:35,552 INFO ReplicaDB:89: Total process time: 1007ms
Compatible Databases
| Persistent Store | Source | Sink Complete | Sink Complete-Atomic | Sink Incremental | Sink Bandwidth Throttling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle | |||||
| MySQL | |||||
| MariaDB | |||||
| PostgreSQL | |||||
| SQL Server | |||||
| IBM DB2 LUW | |||||
| IBM DB2 for i | |||||
| SQLite | |||||
| MongoDB | |||||
| CSV | |||||
| Denodo | |||||
| Kafka | |||||
| Amazon S3 | |||||
| JDBC-Compliant database |
Supported feature . Unsupported feature . Not applicable feature blank
Contributing
We welcome contributions to ReplicaDB! Whether you’re fixing bugs, adding features, or improving documentation, your help is appreciated.
How to Contribute:
- Fork the repository: https://github.com/osalvador/ReplicaDB
- Create your feature branch:
git checkout -b feature/your-feature-name - Commit your changes:
git commit -am 'Add feature description' - Push to the branch:
git push origin feature/your-feature-name - Create a Pull Request
Contribution Guidelines:
- Follow existing code style and conventions
- Add tests for new functionality
- Update documentation to reflect your changes
- Ensure all tests pass before submitting PR
- Keep pull requests focused on a single feature or fix
For detailed guidelines, see CONTRIBUTING.md (when available).
License
ReplicaDB is open source software released under the Apache License 2.0. You are free to use, modify, and distribute this software for both commercial and non-commercial purposes, subject to the terms and conditions of the license.
Key points:
- Free for commercial and personal use
- Modification and distribution permitted
- Must include license and copyright notices
- Provided “as is” without warranty
For complete license terms, see the LICENSE file in the repository.
